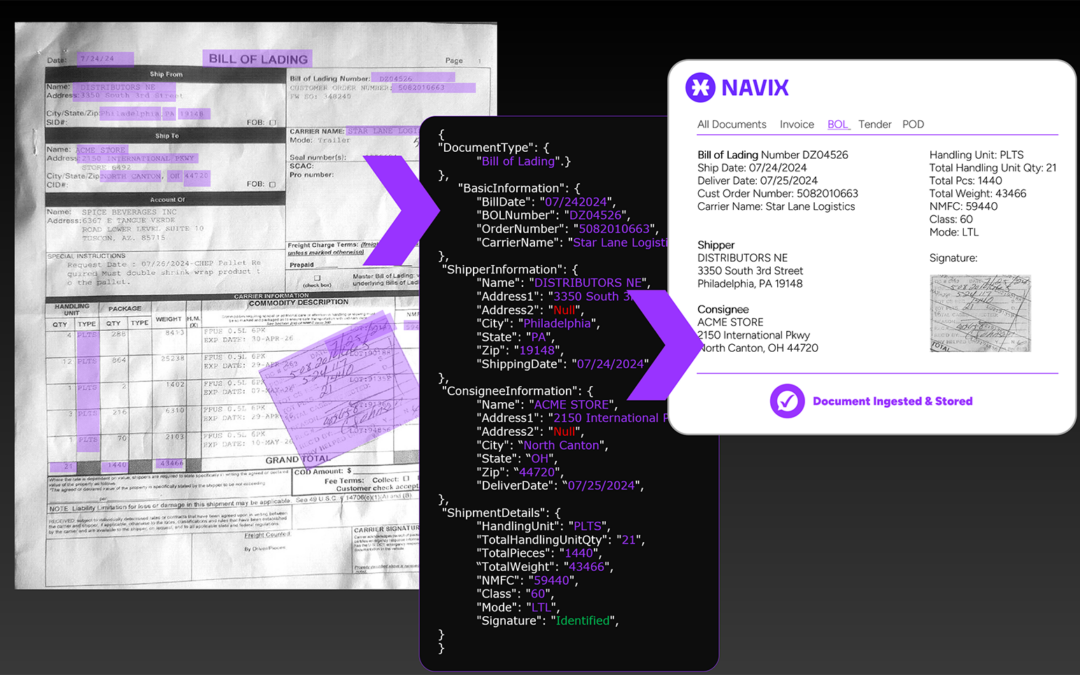
As a part of the artificial intelligence technology family, machine learning enables computers to learn new tasks without being explicitly programmed. Below is an article explaining machine learning and how Navix integrates it into its freight audit automation system.
What Is Machine Learning?
Machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence where systems “learn” from data, statistics, and trial and error to optimize processes and innovate more rapidly. Through machine learning, computers can apply human-like reasoning and decision-making to address some of the world’s most challenging problems, from cancer research to climate change.
Most computer programs rely on code to dictate their actions and the information they retain, known as explicit knowledge, which includes anything easily written or recorded, such as textbooks, videos, and manuals. With machine learning, computers acquire tacit knowledge, or knowledge gained from personal experience and context, which is difficult to transfer through written or verbal communication.
How Does Machine Learning Work?
Machine learning compiles input data from various sources, such as training sessions, data set search engines, websites, and open data registries. This data functions similarly to prior experiences for humans, providing historical information for machine learning models to use when making future decisions.
Algorithms analyze this data, identifying patterns and trends to make accurate predictions. For example, Navix uses machine learning to analyze carrier documents such as bills of lading, PODs, re-weight certificates, and more. These documents are read by AI, and the system’s performance improves with more data. Typically, the larger the data set a carrier can provide to the machine learning software, the more accurate the document readability.
The goal is for machine learning algorithms to perform these tasks independently, requiring minimal human intervention. This accelerates various processes as machine learning automates many aspects of different industries.
Types of Machine Learning
There are several types of machine learning, varying based on factors like data size and diversity. Below are some common types of machine learning under which popular algorithms can be categorized.
Supervised Learning
Supervised learning involves mathematical models of data containing both input and output information. Machine learning programs are continuously fed these models, enabling them to predict outputs based on new inputs
Regression and classification are two popular analyses under supervised learning. Regression analysis is used to discover and predict relationships between outcome variables and one or more independent variables. Commonly known as linear regression, this method provides training data to help systems with predicting and forecasting. Classification trains systems to identify objects and categorize them. For instance, email filters use machine learning to automate the sorting of incoming emails into primary, promotion, and spam inboxes.
Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning involves data containing only inputs, which is then structured through clustering or grouping. This method learns from unlabeled or uncategorized test data, grouping raw data based on commonalities. Cluster analysis uses unsupervised learning to sort through large datasets and group certain data points together. Clustering is a popular tool for data mining, used in everything from genetic research to creating virtual social media communities of like-minded individuals.
Semi-Supervised Learning
Semi-supervised learning falls between unsupervised and supervised learning. This technique involves feeding programs a mixture of labeled and unlabeled data, speeding up the machine learning process and improving accuracy in object identification.
Typically, a small amount of labeled data is introduced alongside a large percentage of unlabeled information. The computer uses the structured data to cluster the remaining information. Labeling supervised data is a significant undertaking due to high costs and extensive time requirements.
Machine learning is just one subset of artificial intelligence, and multiple subsets can be deployed simultaneously depending on the desired outcome. For Navix, freight audit automation combines machine learning with predetermined dynamic business rules, allowing for the autonomous flow of documents without human intervention. This technology enables third-party logistics providers to improve the days-to-bill metric, generating substantial working capital. Navix eliminates manual touchpoints and processes that burden finance and audit teams while reducing common errors that may have downstream effects.
Sources: https://builtin.com / https://www.dataversity.net/